

Research examining brain scans show low blood flow in the hippocampus of marijuana users, which adversely affects memory. When someone experiences severe low mood, their hippocampus loses volume.Īdditionally, research shows that being severely overweight may cause memory loss and damage to the hippocampus.Įven brief periods of sleeplessness can have long-lasting consequences on the hippocampus such as impaired memory consolidation.Ĭonsuming too much sugar can adversely affect your hippocampus function too, negatively impacting your memory recall. 50 to 75 percent of people who suffer from neurological issues that cause abnormal brain activity show damage to the hippocampus. They also can lose the ability to navigate from one place to another. When it begins shrinking in size, a person begins to lose their short-term memory. The hippocampus is one of the first areas to be affected with the onset of memory-related neurodegenerative issues. Extreme stress can disrupt the process of new cell growth, so you don’t make as many new nerve cells as you should. In a healthy brain, 700 new nerve cells are created every day in the hippocampus, which is critical to forming memories. Long-term exposure to high levels of stress is associated with the loss of hippocampal volume, according to one study. The hippocampus is one area that shows some of the most significant loss that worsens in advanced age. Our total brain volume begins to shrink when we’re in our 30s or 40s and accelerates around age 60. Several health conditions and lifestyle choices can adversely affect your hippocampus, and, therefore, your memory function. The hippocampus is a powerful yet sensitive part of the brain, making it susceptible to damage.
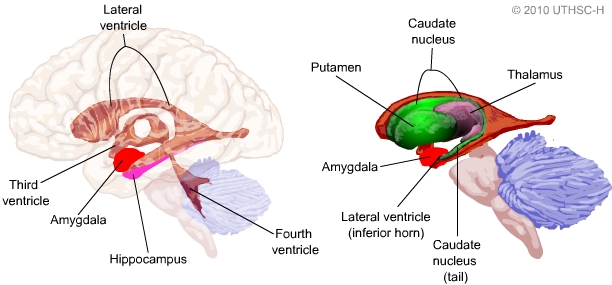
Hippocampus anatomy and function drivers#
Interestingly, brain scans have shown that some taxi drivers have an enlarged hippocampus compared to non-taxi drivers, due to the spatial memories required to do their job! The Hippocampus Is Vulnerable It appears that neurons in the hippocampus encode information about our environment in such a way that they create a mind map of our surroundings. Spatial relationship memories involve pathways or routes. Declarative memories are both episodic (memories created from things you experience personally) and semantic (facts and information). The hippocampus helps us to process and retrieve two kinds of memory: declarative memories and spatial relationships. In basic terms, the hippocampus is where your short-term memories and new learning are turned into long-term memories that are then stored elsewhere in the brain. It plays a vital role in regulating learning, memory encoding, memory consolidation, and spatial navigation. The term hippocampus originates from the Greek word hippokampus ( hippo meaning “horse” and kampos meaning “sea monster”) as the shape of the hippocampus resembles that of a sea horse.Ībout 1.5 to 2 inches in length, the hippocampus is embedded deep within the temporal lobe of your brain. Here’s what you need to know about this funny sounding brain structure. If you want to take good care of your brain, gaining a basic understanding of its structures and the types of functions they manage and control is a great place to start.įor memory, a top brain health concern, the hippocampus plays a key role.
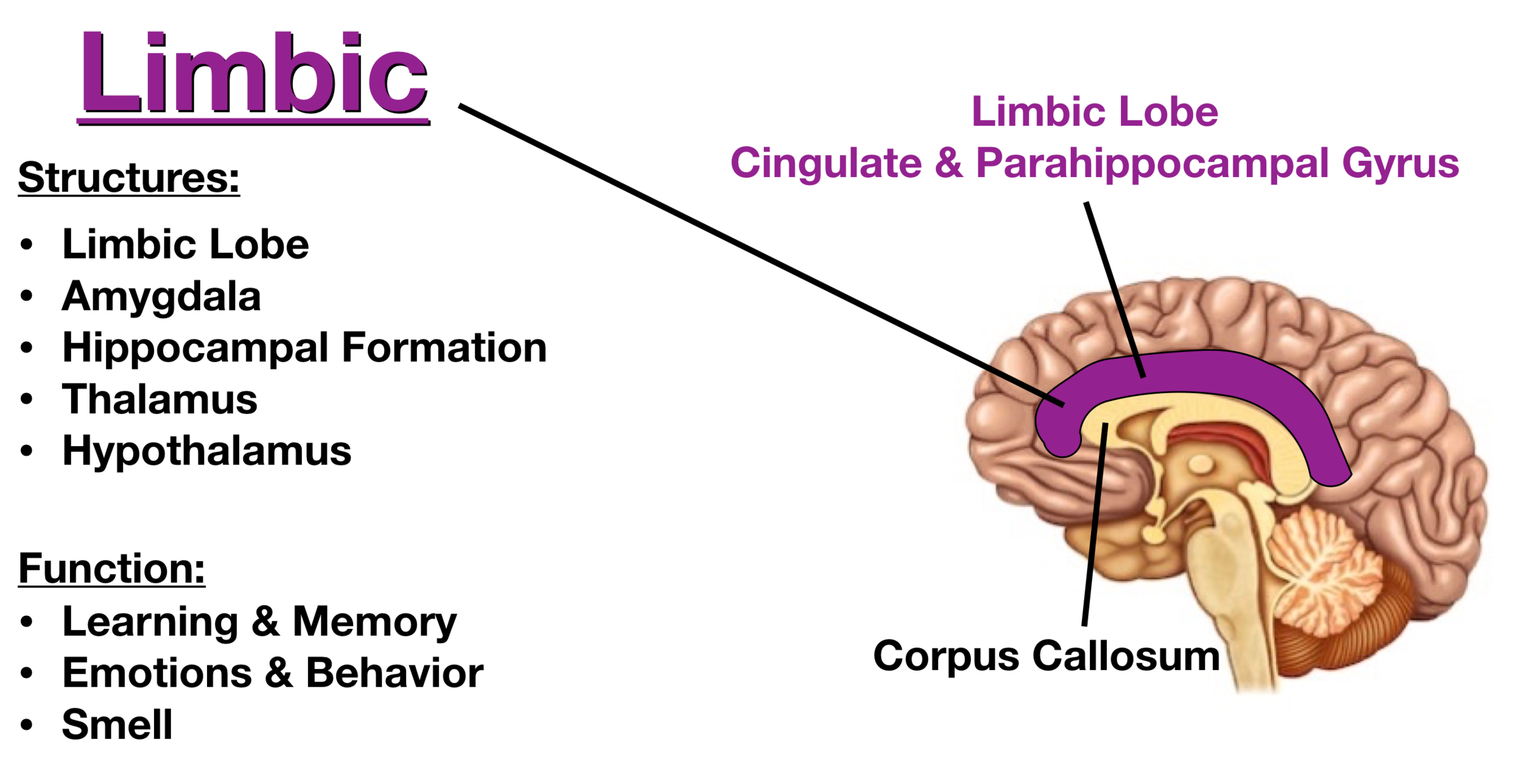

However, when it comes to brain anatomy, there’s a lot we all can learn. Most of us know our body’s anatomy – the major organs, bones, and perhaps even a few muscles.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
